Publishing a game on Steam is a major milestone for many indie developers. As the largest PC gaming storefront, Steam offers access to a global audience. At the same time, the process involves more than simply uploading a build and pressing a release button.
To publish game on Steam in a predictable and controlled way, developers need to complete financial verification, prepare a store page that converts, and plan a launch that fits both market conditions and Steam’s discovery mechanics. This guide focuses on the practical steps required to move from preparation to release with fewer assumptions and more clarity.

Step 1: Steam Direct Fee and Administrative Setup
Before uploading any content, developers must complete Steam Direct, Valve’s onboarding and verification process. This step exists to confirm identity and reduce low-quality or spam submissions on the platform.
Paying the Steam Direct fee
Valve requires a $100 USD fee for each game submitted. This fee functions as a recoupable deposit rather than a permanent cost. Once a title generates $1,000 USD in adjusted gross revenue, the fee is returned.
Before committing, it is useful to evaluate whether a game concept has realistic revenue potential within its genre. Comparing similar titles can help determine whether reaching this threshold is common or exceptional.
Tax and banking information
Completing the tax interview is mandatory before you can publish game on Steam.
- US-based developers must provide an SSN or EIN.
- Developers outside the US need a valid TIN to benefit from tax treaties and avoid default withholding.
Incorrect or incomplete information at this stage can delay payouts after launch.

Step 2: Creating a High-Converting Store Page
A Steam store page is more than a presentation layer. At launch, visibility alone is rarely enough. Click-through rate and purchase conversion determine whether impressions turn into results.
Capsule art and trailer basics
The main capsule image is often the first element players see. If it appears unpolished or unclear, players may assume the same about the game itself.
Trailers should prioritize gameplay immediately. The opening seconds matter more than logos or studio introductions, especially for first-time viewers.
Tags and descriptions
Steam functions as a search-driven platform. Tag selection directly affects where and to whom your game is shown.
Using specific, genre-defining tags helps align your game with the right audience. Descriptions should reflect core mechanics and themes naturally, rather than forcing keywords. To validate tag choices, Datahumble can be used to analyze which tags drive traffic for top-performing games in the same category.
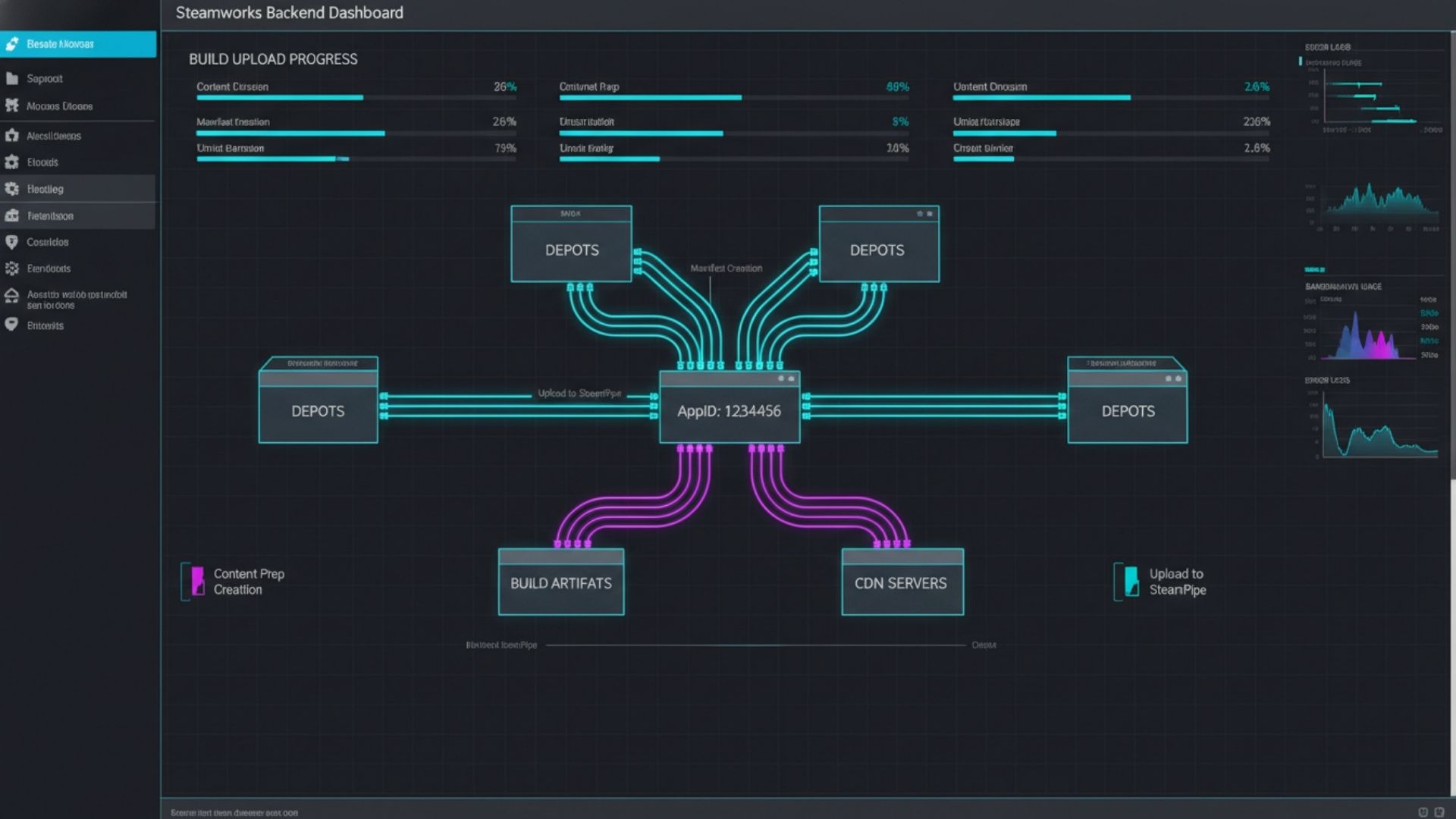
Step 3: Uploading Builds and Configuring Steamworks
Once paperwork and store assets are prepared, the technical upload process begins.
Depots and builds
Each game is assigned an AppID, one or more depots for platform-specific files, and builds associated with those depots. Correct configuration ensures Steam launches the right executable and delivers updates properly.
Uploading with SteamPipe
SteamPipe provides a graphical interface for uploading builds without command-line complexity. After uploading, builds must be marked live in the backend before they can be reviewed.
Step 4: Pricing Strategy and Release Timing
Pricing is a strategic decision that influences perception, discount flexibility, and long-term performance.
Pricing too low can signal limited value, while pricing too high may restrict early adoption. Many indie titles cluster within mid-range price tiers depending on scope and genre. Rather than relying on instinct, developers benefit from benchmarking against comparable titles. Datahumble allows you to review genre medians and observe how pricing aligns with performance patterns.
Regional pricing considerations
Steam suggests automatic regional pricing, but these defaults are not always optimal. In regions such as LATAM or MENA, unadjusted prices may exceed local purchasing power.
Release timing considerations
Thoughtful regional adjustments can improve unit sales without undermining global positioning. Timing affects visibility. Launching during major sales events or alongside large AAA releases can reduce exposure in the New Releases feed. Choosing a quieter window often improves initial discoverability.
Step 5: The Coming Soon Phase and Wishlist Growth
Before you publish game on Steam, your store page should remain in Coming Soon status long enough to accumulate wishlists. Wishlist activity is a key signal within Steam’s visibility systems.
Wishlist benchmarks
While exact thresholds vary by genre, higher wishlist counts generally improve placement in Popular Upcoming sections. More important than total volume is the rate at which wishlists grow over time.
Steam Next Fest
Participating in Steam Next Fest with a playable demo can significantly increase wishlist momentum. Preparation typically requires a stable, polished demo well ahead of the event.
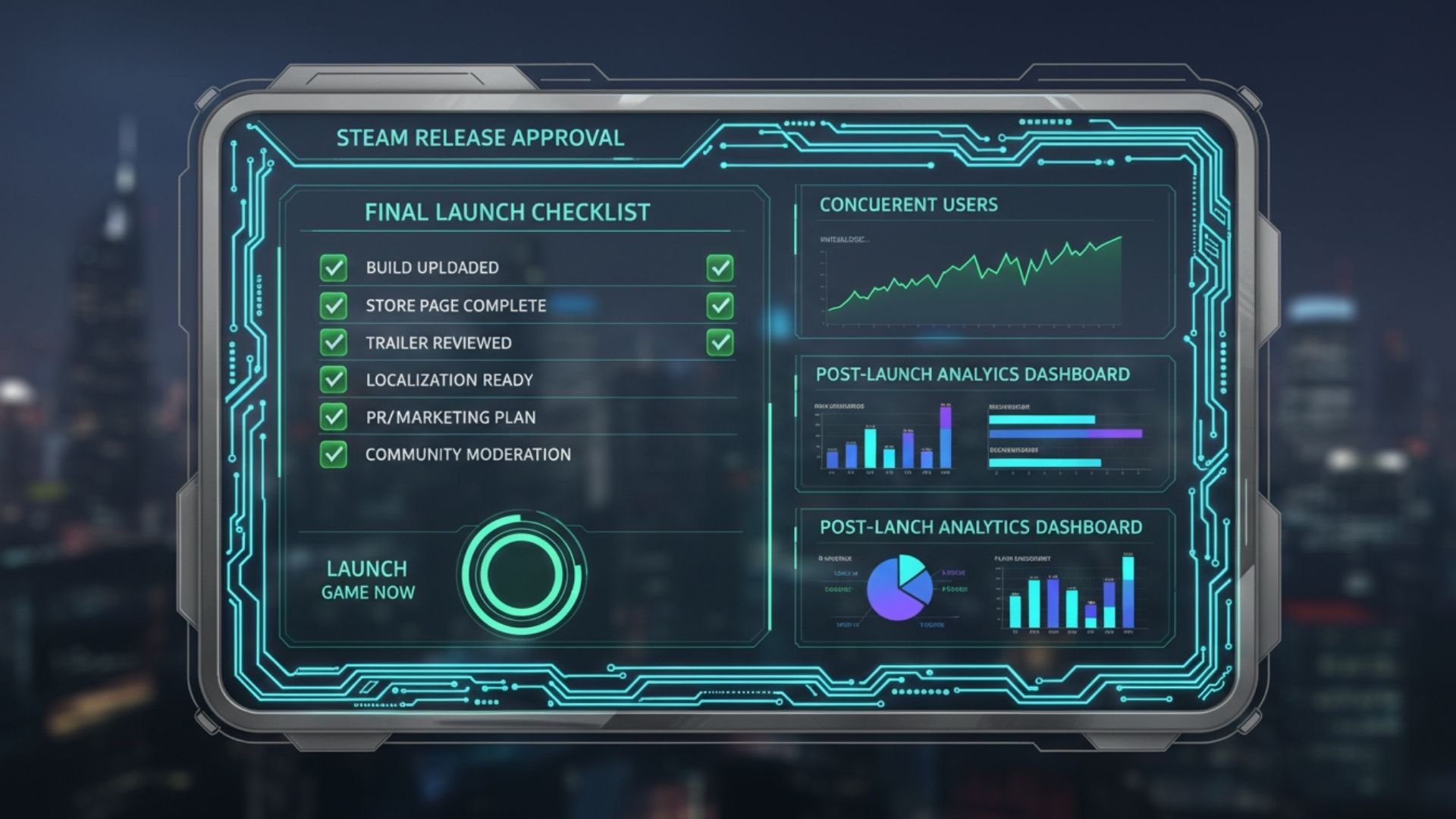
Step 6: Review Process and Launch
Before release, Valve reviews the submitted build to confirm that it launches correctly and meets platform requirements.
Review timelines usually range from a few business days. Builds should be submitted well in advance of the intended release date to avoid delays.
After launch, monitoring metrics such as concurrent users and playtime helps identify early retention or refund risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does it cost to publish a game on Steam?
A $100 USD recoupable fee per game. There are no monthly platform fees.Can I publish a game on Steam for free?
No. The Steam Direct fee is required, although games can be released as free-to-play after approval.Does Steam promote new games automatically?
New releases receive limited initial exposure. Sustained visibility depends on wishlist velocity and sales performance.
Publishing on Steam involves coordinated decisions across pricing, positioning, and timing. Treating the process as a strategic launch rather than a checklist reduces risk and improves outcomes.
Turn your game idea into a measurable launch. Use Datahumble to benchmark pricing, tags, and visibility patterns before release.

